Introduction
Cryptocurrency mining is one of the most critical processes that power blockchain networks. While individual mining rigs once dominated the landscape, today the industry is increasingly driven by large-scale crypto mining facilities. These centers provide the computational power necessary to validate transactions, secure networks, and mint new digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
🔹 What Is a Crypto Mining Facility?
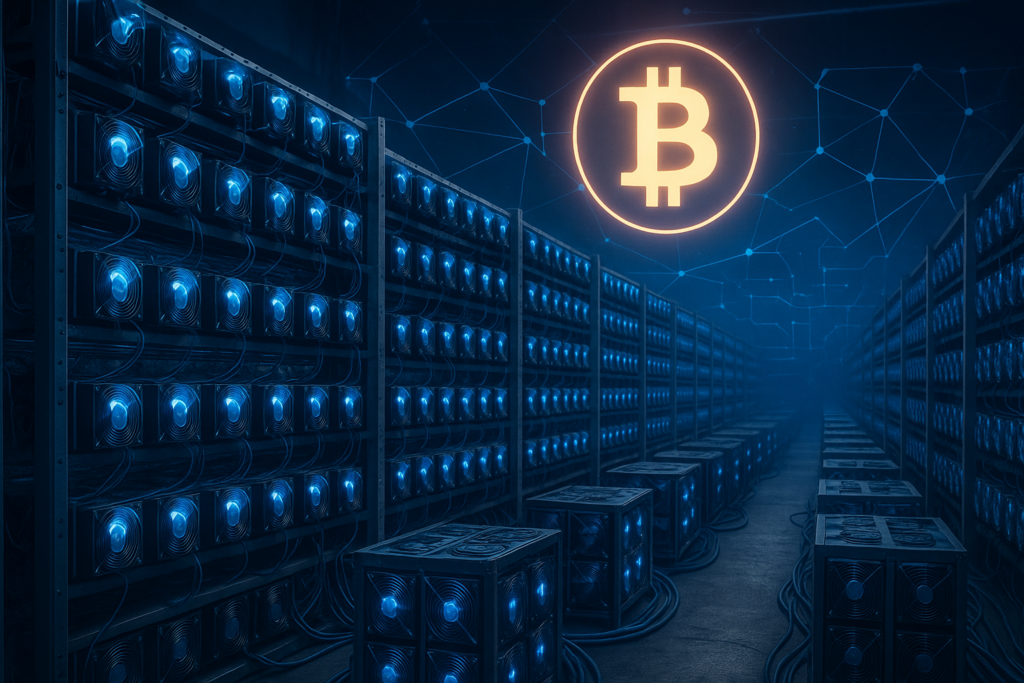
A crypto mining facility is a large-scale data center dedicated to cryptocurrency mining. Instead of a few personal rigs, these facilities can host thousands of mining machines operating 24/7.
Key components include:
- Mining Hardware – ASIC miners or high-performance GPUs.
- Cooling Systems – To manage heat generated by constant computations.
- Power Supply – Access to affordable electricity is crucial for profitability.
- Network Infrastructure – High-speed internet to connect with global blockchains.
💡 Why Mining Facilities Matter
- Security of the Blockchain – They provide the hash power needed to secure decentralized networks.
- Transaction Validation – Facilities confirm and record transactions on the blockchain.
- Scalability – Large operations can sustain the growing demand for computational power.
- Industrialization of Mining – They represent the shift from hobbyist mining to a professional industry.
🌍 Location and Energy Considerations
The success of a mining facility depends heavily on cheap and stable electricity. Many facilities are located in regions with:
- Hydroelectric or geothermal energy (Iceland, Canada).
- Surplus natural gas (Texas, Kazakhstan).
- Cold climates (Russia, Siberia) to reduce cooling costs.
However, this also raises concerns about energy consumption and environmental impact, pushing the industry toward renewable energy adoption.
⚖️ Opportunities and Challenges
✅ Opportunities
- Profitability from mining Bitcoin and altcoins.
- Growth of institutional investments in mining.
- Potential integration with renewable energy projects.
❌ Challenges
- High energy costs and environmental concerns.
- Increasing regulatory scrutiny in countries like the U.S. and China.
- Constant need to upgrade hardware to remain competitive.
📌 Conclusion
Crypto mining facilities are the backbone of blockchain infrastructure, securing networks and enabling digital currencies to operate at scale. While they bring industrial efficiency and stability to mining, they also face challenges in sustainability, regulation, and profitability.
As the crypto industry matures, the future of mining will likely hinge on innovation in energy efficiency and the transition to greener, more sustainable operations.